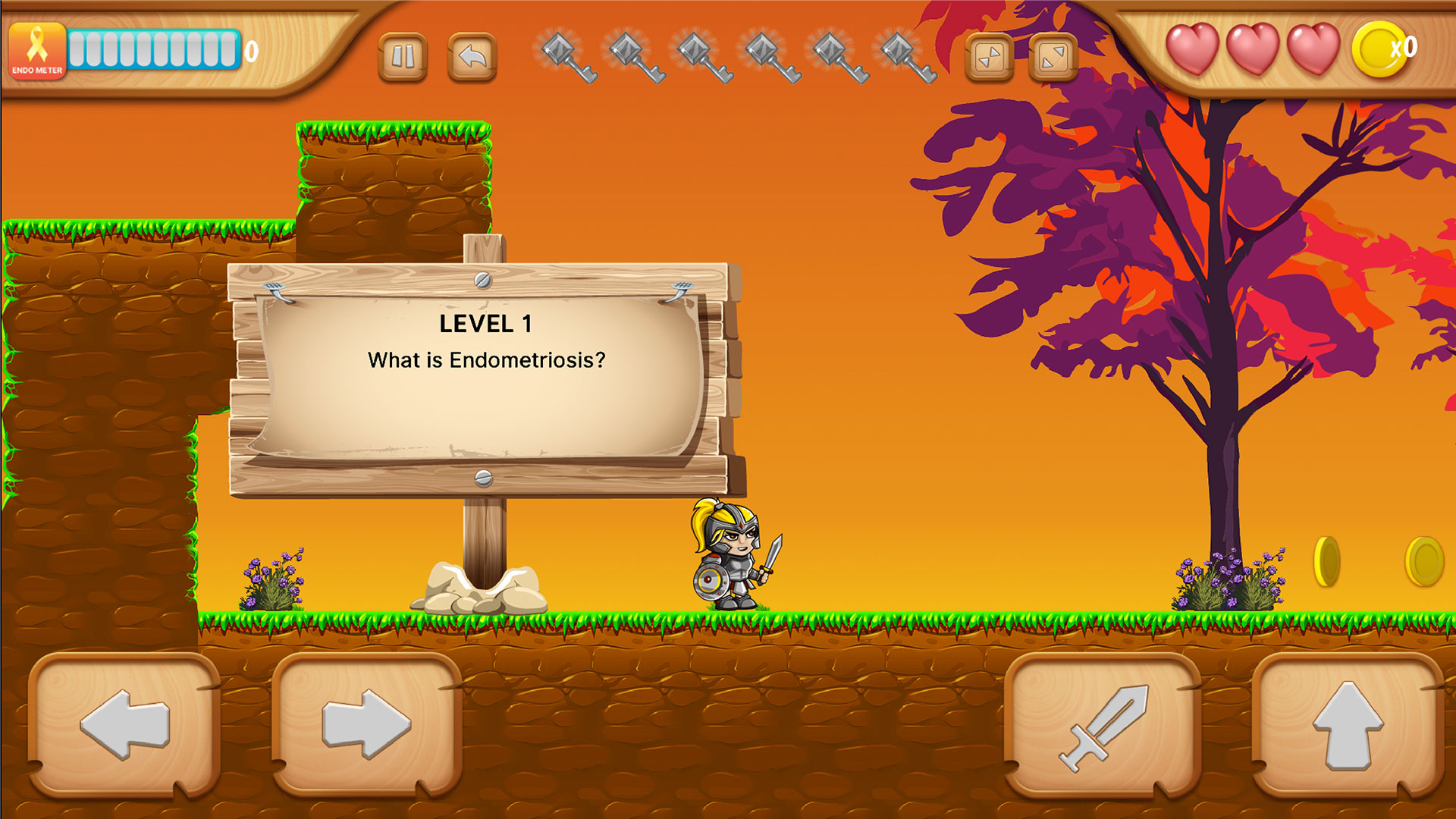
Level 1: What is Endometriosis?
Information Booth 1
Definition of Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a systemic inflammatory condition that is characterized by the presence of endometrium-like tissue that is found in extrauterine sites. It usually shows up as lesions throughout the body and can affect nearly all organ systems. While it’s commonly found in the pelvis and reproductive organs, it can also be found outside the pelvic cavity, which is known as extrapelvic endometriosis.
Information Booth 2
Factors that contribute to Endometriosis
There is no definitive cause of Endometriosis, but it is likely the result of interconnected processes that can include: Genetics, changes during embryonic development, hormones, and maybe environmental factors that can cause genetic changes, called epigenetics.
Genetics
Embryonic development
Endometriosis is found in fetuses and adolescents before they begin menstruation. This is potentially due to tissue misplacement during the embryonic development phase.
Hormones
Elevated levels of estrogen may encourage the development of Endometriosis lesions by an inflammatory process, but it is important to know that high levels of estrogen don’t cause endometriosis. Unfortunately, the lesions make their own estrogen, and lowering systemic estrogen levels may only help with some symptoms.
Environmental Factors (Epigenetics)
Certain environmental factors, such as exposure to toxins or chemicals, may play a role in the development of endometriosis, although research in this area is ongoing.
Conclusion
These factors can interact and vary from person to person, contributing to the complexity of endometriosis. It’s essential for individuals experiencing symptoms to consult your healthcare professionals for diagnosis and management.
Information Booth 3
Risk factors for Endo: age, ethnicity, and lifestyle
Age
Endometriosis doesn’t have an age limit. It can affect teens, adults, and even people after menopause. Most are diagnosed between 25 and 40, but that’s often because it takes years to get answers. Identifying it early, especially in teens, can make a big difference in how it’s managed.
Ethnicity
Endometriosis affects people of all ethnicities. For a long time, it was wrongly called a ‘Caucasian illness,’ but we now know that’s a myth. People of African, Asian, and other backgrounds are also widely affected. Research is still growing, but endo has no racial or ethnic boundaries.
Lifestyle
Certain lifestyle and environmental factors may play a role in endometriosis, though research is still ongoing. Things like never giving birth, having a lower BMI, heavy alcohol use, or smoking have been linked in some studies. Stress, exposure to hormone-disrupting chemicals (like parabens), and diet may also influence symptoms. These links aren’t fully proven, but healthy habits, stress management, and reducing toxin exposure can help overall well-being.
Information Booth 4
Challenges of diagnosing Endo
Non-Specific Symptoms
Many symptoms of endometriosis, like pelvic pain and irregular periods, can look like other conditions such as IBS, PID, or PCOS. This is why it’s hard to diagnose based on symptoms alone.
Lack of Awareness
Endometriosis is still not widely understood among healthcare providers and the general public. This can lead to delayed diagnosis or misdiagnosis.
No Definitive Test
Currently, there is still no single test for endometriosis. Diagnosis usually involves medical history, a physical exam, imaging like a transvaginal ultrasound (TVS), and sometimes surgery (laparoscopy) to confirm the presence of endometrium-like tissue.
Variability in Symptoms
The severity of endometriosis symptoms can vary widely among individuals. Some may have severe pain, while others may have minimal or no symptoms at all, making it challenging to identify.
Coexistence with Other Conditions
Endometriosis can occur alongside other conditions, which can make diagnosis harder, especially when the main symptoms seem menstrual related.
Stigma and Gender Bias
There can be a stigma associated with menstrual pain, and gender bias in healthcare may result in some women’s symptoms being dismissed or not taken seriously.
Treatment as Diagnosis
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe treatments for symptoms, such as pain relief medications, without conducting a thorough investigation to identify the underlying cause. This can be problematic because a patient may end up on an unnecessary medication.
Information Booth 5
Tests and procedures to detect Endometriosis
Medical History and Symptom Assessment
Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history and discussing your symptoms. This will help them understand your symptoms and their impact on your daily life.
Physical Examination
A pelvic exam may be performed to check for abnormalities, tenderness, or masses that could be indicative of endometriosis.
Imaging Studies
- Transvaginal Ultrasound is one imaging method that involves inserting a wand-like device into the vagina to create images of the pelvic organs. While it can help identify ovarian cysts, it may not detect all instances of endometriosis.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): An imaging method that involves lying down in a large circular device. It creates detailed pictures of the inside of your body using a strong magnet, radio waves, and a computer to produce these images. Like transvaginal ultrasound, not all types of endometriosis can be found. This type of imaging is good for cysts and nodules.
Laparoscopy
Often considered the gold standard for diagnosing all forms of endometriosis, laparoscopy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure in which a thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdominal wall. The surgeon can visually identify and remove lesions, scar tissue, and adhesions, confirming the diagnosis. However, the skill and experience of the surgeon are crucial for accurately diagnosing endometriosis.
Note that while laparoscopy is still seen as the gold standard, in many countries, advanced imaging options like MRI and Trans Vaginal Ultrasound, when conducted by trained endometriosis excision specialists, can effectively detect deep infiltrating endometriosis and serve as viable diagnostic alternatives.
Biopsy
Taking a biopsy during surgery is the most definitive way to know that abnormal tissue is actually endometriosis. During a laparoscopy, tissue samples (biopsies) may be taken for examination in a laboratory to confirm the presence of endometriosis.
Conclusion
Remember that diagnosing endometriosis can be a complex process, and it may require a combination of these tests and procedures.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare provider who specializes in the condition to determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach for your specific case.
Early diagnosis and management can help improve the quality of life for individuals with endometriosis.
Information Booth 6
Importance of seeking a diagnosis
Seeking a diagnosis for suspected endometriosis is crucial for several reasons:
Pain Management
Endometriosis often causes severe pelvic pain, menstrual cramps, and pain during sexual intercourse. It can also cause more unusual symptoms, such as painful urination and bowel movements. A proper diagnosis can lead to effective pain management strategies, improving your quality of life.
Fertility Preservation
For individuals who wish to conceive, early diagnosis and management of endometriosis can help preserve fertility by addressing any reproductive issues associated with the condition.
Treatment Options
A confirmed diagnosis allows healthcare providers to tailor treatment options to your specific needs. This can include medications, hormonal therapy, or surgical interventions.
Preventing Disease Progression
Identifying endometriosis early can help reduce the risk of worsening pain, organ involvement, and complications, and may improve quality of life.
Emotional Well-Being
Living with chronic pain and no answers can be tough on one’s mental health. Getting a diagnosis and treatment plan can bring relief, reduce anxiety, and give hope for better days ahead.
Support and Education
A diagnosis can connect you with support groups, healthcare professionals, and resources dedicated to endometriosis. These can offer valuable information, emotional support, and guidance.
Monitoring and Management
Endometriosis is a chronic condition that may require ongoing attention. Regular check-ups and monitoring may be important to tracking its progression and adjusting treatment as needed.
In summary, seeking a diagnosis of endometriosis is vital for addressing symptoms, preserving fertility, and improving your overall well-being.
If you suspect you have endometriosis or are experiencing symptoms, consult with a healthcare provider who specializes in the condition for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate care.